Part-1 of the blog mini-series on RED-S
By Dr Nicky Keay
It is hard to dispute that women are underrepresented in medical research and certainly there are not many studies that include female athletes. Does this matter? After all whatever your gender, the same physiological and metabolic processes occur. However, the Endocrine system is where there are distinct differences in sex steroid production, which in turn have different responses in multiple target cells.
Although studies on changes in exercise performance in response to various dietary interventions and training regimes are often very interesting and well described, I am left feeling slightly uneasy when the subjects are all males. The cause for my concern is that the female hypothalamus-pituitary-ovarian axis is a particularly sensitive system with complex feedback loops and interacting networks.
Menstrual disturbance is not unusual amongst women in sport/dance where low body weight is an advantage. When a ballet dancer performs pointe work, putting full body weight through the big toe is hard enough, without extra load! Some women might consider it a convenience to be spared the hassle of menstruation. At age 24, I was perfectly fine never having had a period (primary amenorrhoea), or so I thought, being no more tired than other hospital medical colleagues working full time, studying for postgraduate medical exams and also involved in exercise training.

While working as a SHO at Northwick Park Hospital, I volunteered to be included in a study at the British Olympic Medical Association. The study was of female lightweight rowers and ballet dancers to look at VO2 max, percentage body fat and bone mineral density (BMD). I had been doing Ballet intensively (and obsessively) from a very young age, together with restricted fat and carbohydrate intake. Sounds a familiar scenario? Although I looked perfectly healthy (and I did not fit into a clinical condition requiring treatment), worked and danced well, my bone density was worryingly low. So if you are a female doing weight-bearing exercise or resistance training which loads the skeleton, these activities promoting osteogenesis will be negated if you are not ovulating and producing adequate oestrogens. The female athlete triad composed of disordered eating, amenorrhoea and low BMD was originally described by Drinkwater in 1984. However, once pathological states causing amenorrhoea have been excluded, in medical terms the female athlete triad did not necessarily constitute a disease state requiring intervention, rather subset of the “normal population”.
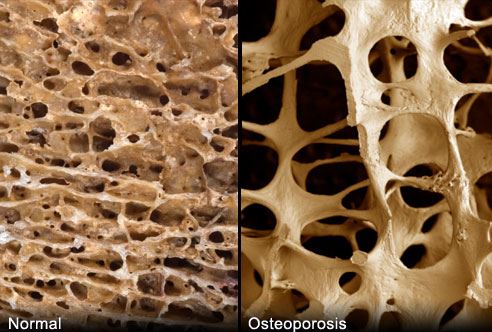
How significant is having low BMD compared to the age-matched population during your 20s? Could this even be viewed as a reversible adaptation to training, reflected in site specific differences in BMD according to sport? After all, when female athletes retire with decreased training “stress” and more “relaxed” diet, menses often resume and therefore does BMD also improve? This was the question I sought to answer in my study on 57 premenopausal retired professional dancers. Even with return of menses, if these athletes had experienced previous amenorrhoea of more than 6 month duration, then bone loss was irrecoverable. Current low BMD was also correlated to lowest body weight (independent of amenorrhoea) during dance career and later age of menarche. There did not appear to be any protective effect of being on the oral contraceptive pill. Constructing a model of BMD using multiple regression 33.6% of total variation in z (age matched) score for BMD at lumbar spine was accounted for by duration of amenorrhea, age at menarche and lowest body weight during dance career. So “athletic” hypothalamic amenorrhea rather than being a reversible, adaptive response has long term, irreversible effects on BMD.
Apart from bone metabolism, what other systems are impacted by mismatch of energy intake and expenditure in overtly healthy athletes? Are the endocrine and metabolic systems in male athletes also affected by subtle imbalances in training energy expenditure and dietary intake? What about young athletes? In my next blog I will explore the rationale behind the original female athlete triad now being described as part of Relative Energy Deficiency in sports (REDs). The implications for current health and sports performance, as well as long term health in both adult men and women and young athletes.
References
Keay N, Fogelman I, Blake G. Bone mineral density in professional female dancers. British Journal of Sports Medicine, vol 31 no2, 143-7, June 1997.
Keay N. Bone mineral density in professional female dancers. IOC World Congress on Sports Sciences. October 1997.
Keay N, Bone Mineral Density in Professional Female Dancers, Journal of Endocrinology, November 1996, volume 151, supplement p5.
Keay N, Bone Mineral Density in Female Dancers, abstract Clinical Science, Volume 91, no1, July 1996, 20p.
Keay N, Dancers, Periods and Osteoporosis, Dancing Times, September 1995, 1187-1189
Keay N, A study of Dancers, Periods and Osteoporosis, Dance Gazette, Issue 3, 1996, 47
Fit to Dance? Report of National inquiry into dancers’ health
Fit but fragile. National Osteoporosis Society
Your body your risk. Dance UK
From population based norms to personalised medicine: Health, Fitness, Sports Performance